Sony Z5 Cameras: These are the cameras used in the TV studio and feed the video through the signal flow to produce an image at the vision mixer the director can then select which camera he wishes to cut to for the next shot. There are four cameras in the studio three pole cameras and one which is situated upon a job arm.
Jib Arm: A jib arm is a large structure that holds a camera at the end and is counter balanced by weights at one end, jib arms are used for wide shots and swooping shots, alot of experimentation can be used in this device.
Cans: Cans are the headphones worn by crew all over the studio and are used to talk through, there are specific commands used between cans and, they must never be used for general chatter.
STOB Box: The STOB box is vital in the studio all the cables from the floor are fed through this box into the control room. Without a STOB box it would b very difficult to get all the cable into the control room
Grid: A grid is on the ceiling and holds all of the studios lights, some grids have movable sections to allow more adventurous lighting however fixed grids are just as efficient and get the job done.
Lights: Lights are obviously another important part of the equipment as without them we would have to rely on house light which deliver awful lighting and the cameras will not pick this up so well. The studio lights are equipt with barn doors allowing the light to be directed to one place. This ensures that we can create a lighting plot to exact specifications
Dimer Pack: The dimer pack simply controls the lights and will trip out if too many lights are being used, the brightest and other functions can also be adjusted here
Monitor: There will be various monitors around the studio, these show the line out from the vision mixer and can be useful on the floor when cameras are asked to match shots. Monitors are also useful in quiz shows for contestants to view VT inserts.
Speakers: The speakers are necessary for playing VT audio and other audio through, speakers can also be rigged to play all audio through or the directors voice if necessary.
Omnidirectional Microphones: Omnidirectional microphones, are mics which can pick up sound from all around as appose to ordinary hand held mics. These small clip on mics are incredibly small, delicate and expensive so should be handled with much care by hosts or contestants.
Tuesday, 16 March 2010
Crew Roles And Resposibilities
Floor Manager: The Floor Managers job is to ensure that everything is going to plan on the floor, the Floor Manager is the directors voice on the floor. Floor Managers will often brief audience members on what to do during the show such as fire escapes and also cuing applause and other commands.
Assistant Floor Manager: An Assistant Floor Manager will usually assist the Floor Manager by doing the jobs the Floor Manager doesn't have time for like keeping a tally on the scores and maybe asking other crew members on the floor if they are okay to begin the show.
Camera Operators: Camera Operators are obviously in charge of getting the shots required for the show common shots for a TV quiz show will be MCU's, CU's, Wide Shots, 2/3 Shots, Over shoulder shots and so on. A Camera Op should always check his shots before the start of the show, so he knows what he can work with.
Assistant Camera Operators: Assistant Cam Ops don't have too much to do other than hold the cable out of the way of the Operator and help with camera movements such as crabbing and pedding. Although a Camera Assist isn't necessary they can be considerably helpful.
Talent: The Talent is basically whoever is in the show (Host/ Contestants) the talents job is simply to perform and make the show an enjoyable viewing experience.
Vision Mixer: Vision Mixers are in charge of cutting between cameras and VT's by the Directors order the Director will give the number followed by the command cut and on this command the VX must cut to that camera, however if the VX feels another shot would be more appropriate he can use his own initiative to get the best shots he feels possible.
Sound Operator: A Sound Op will begin his role by micing up the audience and talent with omnidirectional mics, the audience will have a hanging mic to simply pick up some atmosphere for the show. Once everyone is miced up the Sound Op will run Sound Checks on the audience and individually the talent adjusting there mics accordingly, there is also a master fader so that in the event of a VT placement or so on they can turn the talent right down.
Assistant Sound Operator: A Sound Assist will simply help the Sound Op with levels and micing people up the Sound Assist is a job similar to Camera Assist, it may not be completely necessary however can be helpful in some instances.
Director: The Director is basically the one who runs the show calling shots and checking everyone is doing their jobs properly. The director will work closely with the VX to get the shots needed, but a good Director must always be on the ball and know exactly what is going on to produce a perfect show.
Assistant Director: An Assistant Director will help the Director if he gets lost for words or starts to lose he trail of thought, in essence the Assist Director is another Director basically a back up Director for the show, in case the Director starts to lose where he/ she is going.
DVD Operator: The DVD Op is in charge of queuing the VT inserts for the show making sure they are all in place and ready to be played into the show if a DVD Op messes up they could give the answer to a question away or worse interfere with the format of the show.
Assistant Floor Manager: An Assistant Floor Manager will usually assist the Floor Manager by doing the jobs the Floor Manager doesn't have time for like keeping a tally on the scores and maybe asking other crew members on the floor if they are okay to begin the show.
Camera Operators: Camera Operators are obviously in charge of getting the shots required for the show common shots for a TV quiz show will be MCU's, CU's, Wide Shots, 2/3 Shots, Over shoulder shots and so on. A Camera Op should always check his shots before the start of the show, so he knows what he can work with.
Assistant Camera Operators: Assistant Cam Ops don't have too much to do other than hold the cable out of the way of the Operator and help with camera movements such as crabbing and pedding. Although a Camera Assist isn't necessary they can be considerably helpful.
Talent: The Talent is basically whoever is in the show (Host/ Contestants) the talents job is simply to perform and make the show an enjoyable viewing experience.
Vision Mixer: Vision Mixers are in charge of cutting between cameras and VT's by the Directors order the Director will give the number followed by the command cut and on this command the VX must cut to that camera, however if the VX feels another shot would be more appropriate he can use his own initiative to get the best shots he feels possible.
Sound Operator: A Sound Op will begin his role by micing up the audience and talent with omnidirectional mics, the audience will have a hanging mic to simply pick up some atmosphere for the show. Once everyone is miced up the Sound Op will run Sound Checks on the audience and individually the talent adjusting there mics accordingly, there is also a master fader so that in the event of a VT placement or so on they can turn the talent right down.
Assistant Sound Operator: A Sound Assist will simply help the Sound Op with levels and micing people up the Sound Assist is a job similar to Camera Assist, it may not be completely necessary however can be helpful in some instances.
Director: The Director is basically the one who runs the show calling shots and checking everyone is doing their jobs properly. The director will work closely with the VX to get the shots needed, but a good Director must always be on the ball and know exactly what is going on to produce a perfect show.
Assistant Director: An Assistant Director will help the Director if he gets lost for words or starts to lose he trail of thought, in essence the Assist Director is another Director basically a back up Director for the show, in case the Director starts to lose where he/ she is going.
DVD Operator: The DVD Op is in charge of queuing the VT inserts for the show making sure they are all in place and ready to be played into the show if a DVD Op messes up they could give the answer to a question away or worse interfere with the format of the show.
Studio Protocol And Practice
There are many health and safety issues within the TV studio which must be highlighted to ensure practice in the studio is able to function properly.
Firstly no food or drink should be allowed in the studio if a drink spills it may damage some of the equipment and food may lead to the studio becoming messy, another factor would be running no one should ever run in a studio there are cables all over the places anyone could trip and injure themselves or break valuable equiptment.
Also the talk backs are to be used only for their function they aren't toys and should only be used to contact others when it is completely necessary, also when not in use they should be switched off.
Cameras are yet another vital part of the studio and recording process they should never be pointed at lights as this can damage the silicone chip inside possibly breaking the camera, they should also always be locked if they are not it could damage the ped or lead to a cam tilting up to a light.
Firstly no food or drink should be allowed in the studio if a drink spills it may damage some of the equipment and food may lead to the studio becoming messy, another factor would be running no one should ever run in a studio there are cables all over the places anyone could trip and injure themselves or break valuable equiptment.
Also the talk backs are to be used only for their function they aren't toys and should only be used to contact others when it is completely necessary, also when not in use they should be switched off.
Cameras are yet another vital part of the studio and recording process they should never be pointed at lights as this can damage the silicone chip inside possibly breaking the camera, they should also always be locked if they are not it could damage the ped or lead to a cam tilting up to a light.
Camera Shots And Moves
There are a quite a few common camera shots in TV Quiz Shows here I will show you what these are and explain how they are best achieved, by framing and the rule of thirds.
Framing:
Framing is simple to explain when using the rule of thirds. The rule of thirds is where a shot is divided into nine equal sections, to make it easier to gain the best possible shots using power points these are where the lines meet and generally the biggest areas of focus when viewing a shot.
When framing up for someone in a TV quiz show or simply an MCU or mid shot the eyes should always be on the top third with about three fingers head room above the subject this is the best way of framing and will always give the best results.
Camera Shots:
Medium Close Up (MCU): A medium close up is probably the most common shot used in a TV Quiz Show this shot is taken from the chest to the top of the head and frames the subject up well for a Quiz Show particularly when someone is talking.
Mid Shot (MS): A mid shot probably wouldn’t be used very often in a Quiz show unless a subject was standing because a mid shot is from the hips to the top of the head and obviously in a Quiz show the talent is normally seated.
Wide Shot (WS): Wide shots can often be used as establishing shots for example setting the scene or showing the set in a Quiz show, the can also be used with a tilt or pan when an ad break is ready to be taken or a sting is about to be inserted. Wide shots show a whole person and the surrounding so this is perfect for an introduction/ establishing shot.
Close Up (CU): Close ups are simply zooms on certain objects or talent, in terms of a subject a close up is from the chin to the top of the head so a real close in on what is happening, in a Quiz show this would be used if something was happening on the table or maybe a zoom on a buzzer or other object may be used.
Two/ Three Shot: This is simply what the name states a two or three shot is a shot with two or three people in this would be used in a Quiz show when teams are being introduced and so on or maybe in a quick fire round when any member of a team could answer a question.
Over Shoulder Shot (OSS): Over Shoulder shots are used to add variety and experimentation an OSS is a shot where we appear to be peering over someone’s shoulder on another subject, this can be useful when shots are getting too samey to add some flare to the show.
Camera Moves:
Crab: Crabbing is where the camera on the tripod wheels to the left or the right.
Ped: To ped is the motion of moving the pedestal up or down.
Pan: Panning would be where a camera is stationed in one position but turns to the let or right to provide a swooping motion.
Tilt: A tilt is the opposite to a pan tilting is where a stationed camera swoops up or down to give more variety to changing shot.
Dolly: Dolly is the opposite of a crabbing motion rather than moving left or right the camera will move forwards or backwards a useful term for framing up shots in the studio.
Framing:
Framing is simple to explain when using the rule of thirds. The rule of thirds is where a shot is divided into nine equal sections, to make it easier to gain the best possible shots using power points these are where the lines meet and generally the biggest areas of focus when viewing a shot.
When framing up for someone in a TV quiz show or simply an MCU or mid shot the eyes should always be on the top third with about three fingers head room above the subject this is the best way of framing and will always give the best results.
Camera Shots:
Medium Close Up (MCU): A medium close up is probably the most common shot used in a TV Quiz Show this shot is taken from the chest to the top of the head and frames the subject up well for a Quiz Show particularly when someone is talking.
Mid Shot (MS): A mid shot probably wouldn’t be used very often in a Quiz show unless a subject was standing because a mid shot is from the hips to the top of the head and obviously in a Quiz show the talent is normally seated.
Wide Shot (WS): Wide shots can often be used as establishing shots for example setting the scene or showing the set in a Quiz show, the can also be used with a tilt or pan when an ad break is ready to be taken or a sting is about to be inserted. Wide shots show a whole person and the surrounding so this is perfect for an introduction/ establishing shot.
Close Up (CU): Close ups are simply zooms on certain objects or talent, in terms of a subject a close up is from the chin to the top of the head so a real close in on what is happening, in a Quiz show this would be used if something was happening on the table or maybe a zoom on a buzzer or other object may be used.
Two/ Three Shot: This is simply what the name states a two or three shot is a shot with two or three people in this would be used in a Quiz show when teams are being introduced and so on or maybe in a quick fire round when any member of a team could answer a question.
Over Shoulder Shot (OSS): Over Shoulder shots are used to add variety and experimentation an OSS is a shot where we appear to be peering over someone’s shoulder on another subject, this can be useful when shots are getting too samey to add some flare to the show.
Camera Moves:
Crab: Crabbing is where the camera on the tripod wheels to the left or the right.
Ped: To ped is the motion of moving the pedestal up or down.
Pan: Panning would be where a camera is stationed in one position but turns to the let or right to provide a swooping motion.
Tilt: A tilt is the opposite to a pan tilting is where a stationed camera swoops up or down to give more variety to changing shot.
Dolly: Dolly is the opposite of a crabbing motion rather than moving left or right the camera will move forwards or backwards a useful term for framing up shots in the studio.
DVD Operation And Insert Requirments
DVD operation is vital for the VT inserts. The DVD op should always be on the ball and know exactly what they are doing, letting the director know when the DVD is ready and so on.
Without a DVD op the process of adding inserts could be very hectic, there should also always be black before and after a clip to allow time for the operator to pause the DVD at the points needed.
Once a clip has been played the Operator should get straight to work queing up the next clip for the show and using the call "DVD ready" to let the director know the VT is lined up.
The inserts are put together on a show reel in some sort of editing software and then exported as a quicktime MOV and added to a DVD in tracks once this is complete a Cue Sheet is produced to let the operator know how long clips are what they contain and so on all this makes the job of DVD op much simpler.
Without a DVD op the process of adding inserts could be very hectic, there should also always be black before and after a clip to allow time for the operator to pause the DVD at the points needed.
Once a clip has been played the Operator should get straight to work queing up the next clip for the show and using the call "DVD ready" to let the director know the VT is lined up.
The inserts are put together on a show reel in some sort of editing software and then exported as a quicktime MOV and added to a DVD in tracks once this is complete a Cue Sheet is produced to let the operator know how long clips are what they contain and so on all this makes the job of DVD op much simpler.
Directing And Directors Calls
Cut: The director uses this command when he wants the vision mixer to cut to another camera the director will say "cut cam 1" for example and the vision mixer will know exactly what to do. These shortened commands are much easier than stating a long sentance.
Crab: Crab means the director wishes a camera to crab he will address the camera op and then tell them how the wish for them to crab or what shot to go for normally in an abreviated form.
Ped: This is simply the same as the crab call except in this circumstance the director wants the cam op to ped up or down maybe to get a more well framed shot or once again a certain shot.
Roll VT: When a director uses the call roll VT he is addressing the DVD operator to play the VT insert the DVD op must be prompt and know exactly when the director is going to cue him.
Cue: Cue can be used in many ways, for example talking to the FM to say cue appluase or cue host, or even the DVD op to roll the VT insert.
Crab: Crab means the director wishes a camera to crab he will address the camera op and then tell them how the wish for them to crab or what shot to go for normally in an abreviated form.
Ped: This is simply the same as the crab call except in this circumstance the director wants the cam op to ped up or down maybe to get a more well framed shot or once again a certain shot.
Roll VT: When a director uses the call roll VT he is addressing the DVD operator to play the VT insert the DVD op must be prompt and know exactly when the director is going to cue him.
Cue: Cue can be used in many ways, for example talking to the FM to say cue appluase or cue host, or even the DVD op to roll the VT insert.
Programme Rundowns
The programme rundown is a simple list of the order the show will run in the rundown will include details on VTs such as length and description of what is in the clip, as well as timings as to when to que inserts, the programme rundown is essetially a script for the show as a whole a running order of what comes after what.
Programme rundowns are essetial for a show to operate without this no one would know the order of the show and everything may be in risk of falling apart.
Programme rundowns are essetial for a show to operate without this no one would know the order of the show and everything may be in risk of falling apart.
Floor Plans
Planning Camera Placement And Shots
When planning placement and shots there is alot that should be taken into consideration firstly who the cam will be pointing at this will determine the use of shots, for example if it is a host cam it will more than likely be on an MCU for the majority of the show.
In our studio there are four cameras and all will be used for the quiz show I shall take you through the subjects and shots of each cam.
Camera 1 & 3: These two cameras essentially have the same job their focus is on the contestants on either side of the host, the shots most common from these cams will be two shots and OSS, however MCU's and possible even three shots can be gained from these cameras.
Camera 2: Camera 2 is the host camera and therefore is placed directly in front of the host, The main shot from here will normally always be an MCU, this can be used for a safety shot if the director does not know where to cut. Another shot from here may also be three shots of either team this could be very useful and experimental during a quickfire round in the quiz show.
Camera 4: This camera is in charge of mainly wide shots but can also be used for swooping shots of the studio when cutting to an ad break for instance. This camera is placed upon a job arm to provide more height and experimentation.
In our studio there are four cameras and all will be used for the quiz show I shall take you through the subjects and shots of each cam.
Camera 1 & 3: These two cameras essentially have the same job their focus is on the contestants on either side of the host, the shots most common from these cams will be two shots and OSS, however MCU's and possible even three shots can be gained from these cameras.
Camera 2: Camera 2 is the host camera and therefore is placed directly in front of the host, The main shot from here will normally always be an MCU, this can be used for a safety shot if the director does not know where to cut. Another shot from here may also be three shots of either team this could be very useful and experimental during a quickfire round in the quiz show.
Camera 4: This camera is in charge of mainly wide shots but can also be used for swooping shots of the studio when cutting to an ad break for instance. This camera is placed upon a job arm to provide more height and experimentation.
Planning Audio Coverage
When planning audio coverage the VT inserts should be tested to see that the levels are at a good range normally between, -6 and +9dB this is the perfect range for any audio in the studio.
Sound checks are another perfect and vital part of planning audio these determine how loud or soft someones voice may be throughout the show and this will help the sound ops adjust accordingly.
Sound checks are another perfect and vital part of planning audio these determine how loud or soft someones voice may be throughout the show and this will help the sound ops adjust accordingly.
Talk-Backs And Their Use/ Protocol
Talk Backs or cans are headphones worn by most members of the crew so that they can communicate efficiently the director will be the main person to talk on cans as will the floor manager it is vital that the floor manager and director always have contact in case there is an emergancy on the studio floor.
Talk backs should only ever be used when appropriate not just for social chat as someone may miss an important call from the director, cameras also should only speak if they need to a simply nod from the camera is enough for the director to know if they understand or not.
Talk backs should only ever be used when appropriate not just for social chat as someone may miss an important call from the director, cameras also should only speak if they need to a simply nod from the camera is enough for the director to know if they understand or not.
Planning And Designing A Set
When panning and designing a set the main thing that needs to be thought about is the colours will they stand out or look good on camera some colours such as white can bounce light and other may not be visable like yellows and other light colours.
When the set designer thinks of an idea they need to draw up a plan in which everyone in the production can understand the set can then be discussed and the team can come to a final conclusion.
Once a set has been planned then it needs to be created the set designers need to begin painting and make sure they stick to a strit deadline to ensure the set is ready for the final show.
When the set designer thinks of an idea they need to draw up a plan in which everyone in the production can understand the set can then be discussed and the team can come to a final conclusion.
Once a set has been planned then it needs to be created the set designers need to begin painting and make sure they stick to a strit deadline to ensure the set is ready for the final show.
Planning And Lighting The Set
Planning the lighting for a set can be tricky depend on what you want. The best method however for testing lighting is to have a monitor riged up to the line out of a camera this way you can see exactly what the lighting will look like on record.
The main lighting used for our quiz show will be that of three point lighting this as the name suggests requires three lights a Key Light, Fill light and Back light.
Key Light: This is a hard light or spotlight and provides the main lighting in this sequence, giving shape to the talent.
Fill Light: The fill light is used to adjust the contrast on the subject addingyet more depth.
Back Light: Finally the back light which makes the subject stand out from the background, also this will give even more depth thus finishing off the three point lighting.
So there you have it there are the three lights used for three point lighting below is an image of how the lighting may be set up.
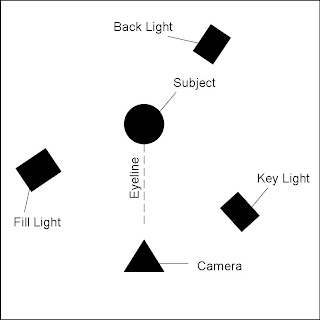
The main lighting used for our quiz show will be that of three point lighting this as the name suggests requires three lights a Key Light, Fill light and Back light.
Key Light: This is a hard light or spotlight and provides the main lighting in this sequence, giving shape to the talent.
Fill Light: The fill light is used to adjust the contrast on the subject addingyet more depth.
Back Light: Finally the back light which makes the subject stand out from the background, also this will give even more depth thus finishing off the three point lighting.
So there you have it there are the three lights used for three point lighting below is an image of how the lighting may be set up.

Scripts And Calls
Scripts are essetial for the Quiz Show to function, scripts provide various amounts of information crucial to the show, there will be speech, ad lib, insert info, shots and so on located in this script.
The script is mainly used by the director however other members of the crew may need access to it such as a floor manger of sound operators, camera ops can also choose to use this to possible make shots a little easy and predict what the director may want.
The script is mainly used by the director however other members of the crew may need access to it such as a floor manger of sound operators, camera ops can also choose to use this to possible make shots a little easy and predict what the director may want.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


